In this article, we are going to explore the marketing insights and prospects on BI and data warehousing.
In the past, marketing would have meant promoting a product and persuading customers and prospects to acquire it by yelling "buy here!" 'Buy today!' or anything similar. Naturally, we're speaking about decades, hundreds, or even millennia ago. Although the ultimate objectives remain the same, the way organizations conduct marketing nowadays is far more advanced.There are several reasons for such changes in corporate operations. However, data is one of the most important explanations.
Data allows businesses to examine every aspect of their operations, including their consumers, what they're doing well, where they may improve, and how they've progressed over time. But first, let's get down to business - How do enterprises collect, organize, and use this information? Business Intelligence and Data warehousing are the solutions. To expertise knowledge on data warehousing, this online snowflake Training course will aid you in developing the requisite skills for your professional career.
What is the definition of a data warehouse?
A data warehouse is a centralized storage location for integrated data. Data warehouses integrate current and historical data acquired from an organization's various source systems into a single location. They've been designed to make analysis and querying easier. A business intelligence platform frequently starts with a data warehouse. Business Intelligence and Data warehouses function together despite their differences.A conventional data warehouse will have a relational database as well as an ETL solution for BI.
A relational database is one that stores and accesses data relating to other data. The data is organized into tables that can be connected using data that is common to all of them. This makes it easy for organizations or/and analysts to better analyze and obtain fresh insights from available customer data.
An ETL solution is a popular method for combining data from various, different sources into a data warehouse, where it may then be used for BI.
What is BI?
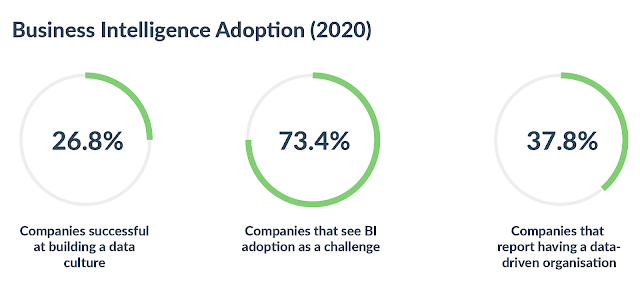
BI (Business intelligence) is a set of technology-driven procedures that take data and turn it into actionable insights that help an organization's tactical and strategic business choices. Business intelligence aims to address a firm's known unknowns. To enable businesses and their decision-makers to find aspects of their business that they had previously overlooked.According to research, one of the most problematic components of business intelligence for 74% of top performers is fragmented or siloed data. This is where business intelligence and data warehousing come together to form a powerful combination. A data warehouse's objective is to allow users to query and analyze enormous amounts of historical data. Data in a warehouse is considered in use since it has been processed for a specific purpose and into a certain format, such as business intelligence.
Some BI software extracts data directly from source applications, while others need the use of a data storage system to aggregate many data sets. A data warehouse, which operates as a central region where BI applications may query and analyze data, is often used to consolidate diverse data sources in BI. Although analytics and reporting tools can function without data warehousing, this can be restricted because data stored in separate systems are often in different forms, making it difficult to draw connections and recognize patterns. Data warehouses clean and standardize data, resulting in more consistent, accurate, and high-quality information. BI processes are streamlined as a result.
BI for Marketing
BI software expands the scope of data analytics above basic organizational analysis. Cindi Howson, an expert in BI, distinguishes between two BI types: Modern BI and Classic (or Traditional) BI.- Traditional BI: Reports are generated by IT specialists using in-house transactional data.
- Modern BI: To analyze data more rapidly, business users work with agile, intuitive systems.
Traditional BI will be used for specific sorts of reporting that require strict accuracy, such as financial reporting. Modern business intelligence, on the other hand, is chosen by marketers who work in a fast-paced environment because it helps them to acquire insight into quickly changing dynamics, behaviors, and information, such as campaign performance or marketing events.
The most frequent BI features we think of when it comes to marketers using BI are reports and dashboards.
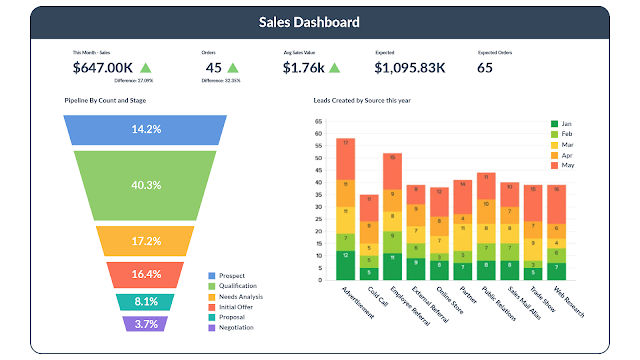
Dashboards are web-based software tools that automatically compile accessible data into graphs and charts that depict the company's current situation. They enable individuals to evaluate data, understand trends, and gain insights into current parts of an organization, such as where sales prospects are now in the pipeline. This month, how many marketing qualified leads have we gained?
They're one-page visualizations that incorporate things like colorful graphs and charts to help decision-makers analyze the campaign or company they're working on. Dashboards can be customized and provide real-time information (viewing what's going on right now). They provide simple KPIs, or information summaries, that allow for quick decision-making and remove the guesswork. Dashboards are much more versatile than reports in that they may be utilized and comprehended by a far larger number of employees within an organization.
Multi-page accounts, on the other hand, are reports. They're usually in document format and are used to collect and present enormous amounts of detailed information. Business analysts are more likely to use reports than other divisions inside a corporation.
Reports are a major data source and can be quite beneficial for business insights; however, the data they provide is not updated in real-time and typically reflects a specific component of a firm, making it more difficult to interpret. A dashboard, on the other hand, can display a variety of metrics from other departments, like sales, marketing, human resources, manufacturing, and so on. Reports must normally be 'run,' which takes time to prepare and export. They are, nevertheless, an excellent alternative if you need to get down to the nitty-gritty details.
While all components of BI are useful for actionable business insights, dashboards are by far the most useful BI feature for marketers. BI dashboards assist marketers in better understanding and visualizing their activities in terms of the business, allowing them to make better decisions based on real data.
But what are the benefits of using BI for marketers?
Insights Into BI: Actionable Analytics
The fascinating data streams and highly visual dashboards offered by business intelligence aren't just for marketers to look at; the analytics that business intelligence provides help marketers, and firms in general, for optimizing business output and strengthening their company.Marketers, who make use of BI insights can get solutions to queries like Do my campaigns result in conversions? Were my KPIs above-target, remaining static, on-target, or below-target? Is the firm’s social media profile expanding and being used?
In addition to providing answers to those ever-present issues, BI provides marketers with access to the following opportunities:
- Better targeting: It's a proven approach to achieve great results if you deliver the appropriate message, at the right time, to the right person. Marketers may use BI to better target consumers depending on real facts. Failing to target the most relevant clients and prospects means your firm is missing a trick, and your competitors would take advantage of the lucrative audiences you overlook.
- Campaign optimization: Marketers can use analytics dashboards to see which campaigns (when, where, why, and so on) are performing best and generating the most leads. Business Intelligence tools enable you to monitor and analyze campaign results in real-time, and also compare them to historical data. This allows you to make enhancements or modifications based on actual historical patterns.
- The enhanced customer experience (CX): Firms all across the world compete to provide the greatest CX. BI gives businesses the resources they need to comprehend their customers and prospects, including their wants, requirements, behaviors, and pain areas, so they can better serve them.
- Streamlined strategies: Companies can use BI to get a comprehensive perspective of their operations and, as a consequence, evaluate performance against rivals and/or goals, and also discover company strengths, threats, opportunities, and weaknesses. You can construct authentic and highly focused marketing campaigns if you have correct data and quick reporting, which warehoused data and BI provides.
- Optimized ROI: When BI is used to achieve the aforementioned goals, firms might see a significant increase in their ROI. Companies can achieve sustainable and steady growth when audiences are well-targeted, marketing is optimized, customer experience is improved, and strategies are streamlined.
But it isn't just about marketing. BI technologies can be used by other departments to get information. Take, for instance, sales. Business development teams must be aware of their prospects' current status in the sales pipeline. The insight that BI provides aids in the optimization of customer acquisition activities and the smoother progression of prospects through the sales funnel.
By allowing diverse teams to view an organization's dashboards and, reports business intelligence may facilitate cross-departmental collaboration.
With cross-departmental dashboard access, marketing, sales, and often other departments can track business activity and identify where, when, and why customers are leaving the customer journey, where marketing qualified leads are being generated, and so on.

No comments:
Post a Comment